📝... Meaning and Definition of Map Projection :-
maps are drawn on a flat surface and represent a part and whole of the earths surface. The spherical shape of the earth is represented on the plane surface by devising and geometrical and mathematical methods to derive a network of latitudes and longitudes upon which an accurate depiction of the earth is made. This process of transformation is known as projection.
The spherical globe can't be represented on a flat surface without losing one or two of it's properties. but the global network of meridian's and parallels represent true shape, equal area, correct distance.
📝 According to F. j. Monkhouse :- " A map projection is the representation of the earth's parallels and meridian's as a net or graticule on a plane surface. "
📝....... According to Erwin Raisz :- " A Projection can be defined as Any orderly system of parallels and meridian's on which a map can be drawn. "
📝...... According to J. A. Steers :- " A map projection is a means of representing the lines of latitude and longitude of the globe on a flat sheet of paper. "
📝.... According to Johan Bygott :- " A map projection is some method of representing on a sheet of paper the lines of latitude and longitude of the globe. "
📝 Classification of Map projection :-
👉 (1.) According to Use of Light :- projection are divided into two parts according to use of light.
[a] Perspective map projection :- a projection can be derived by projecting light through a globe made of glass with graticules marked on it. On to any developable surface. It is called a perspective projection. It is also known as Geometrical Projection.
[b] Non-Perspective Map Projection :- a projection can be derived by meridians and parallels are modified with the aid of mathematics and if the map projection acquires certain other particular properties. It is known as a non -perspective projection.
📝.. (2.) According to Merit :-
Projections are divided into three parts according to merit.
👉[ a ] Orthomorphic projections :- the Orthomorphic projection aims at maintaining the shape of the map surface at any point of the shape of the corresponding point on the earth. The scale should be same at any point in all directions and the angle at which the parallels intersect the meridian's governs the shape of areas. But no projection can provide true shape to large areas like continents. It is called a Conformal Projection.
Examples -
1. Mercator projection.
2. Polar Zenithal projection.
3.Stereographic projection.
👉 [ b ] Homolographic projection :- an equal area map projection aims at preserving the ratio of mapped area to the corresponding earth area. Since area is a product of both length and breadth , we can increase one and diminish the other. Projections with this property are called equal area or Equivalent projection or Homolographic projection.
Exmples -
1. Mollweide Homolographic projection.
2. Sanson flamsteeds sinusoidal projection.
3.Bonnes projection.
4. Polar zenithal equal area projection.
5. Johann Heinrich Lambert cylindrical equal area projection.
👉 [ c ] Azimuthal projections :- the scale is correct in these projections and Azimuthal projections present true bearings. They are called Equidistant projections.
Examples -
1. Mercator projection.
2. Zenithal projection.
📝.. ( 3.) According to the method of construction :- There are three types of map projections according to the area used for transferring the graticule.
[ a ] Conical Projections.
[ b ] Cylindrical Projections.
[ c ] Zenithal projections.
👉 [a] Conical Projections :- These are constructed by projecting part of the globe on to a cone which just touches a circle on the globe. The parallel latitude, around which the cone is tangent to the globe is known as the standard parallel and it is correctly represented on a projection. Other point of the globe are casting there shadows on the cone. When this cone is developed into a flat surface it is a conical projection.
✍️✍️✍️ Types of Conical Projections :-
👉 ( 1.) Conical projection with One standard Parallel :- It is a simple conical projection in this projection the radius of the standard parallel is equal to the radius of the corresponding parallel on a globe of the same scale. The scale is true only along the standard parallel. Since the area are exaggerated away from the standard parallel. It is not suitable for showing countries with a large latitudinal extent.
👉 (2.) Conical Projection with Two Standard Parallel :- By the simple conical projection the area of a country with a large land mass can not be shown correctly. However it can be represented more correctly with two standard parallel and it is constructed with the cone bisecting the surface of the globe. The selection of two standard parallels is very important and it depends upon the purpose of the map and the area to be emphasized. This projection is suitable for larger countries like USA, Canada etc.
👉 ( 3.) Bonne's Projection :- It is a modified version of the simple conical projection. It has only one standard parallel , but each parallel is truly divided and so it is an equal area map projection. The distance between any tow given parallels along the central meridians is true and constant , but the shape is distorted at the edges.
👉 (4.) Polyconic Projection :- this projection is derived by considering the number of cones placed over a globe. Each of these cones is in tangent to it's corresponding latitude , there by making each.
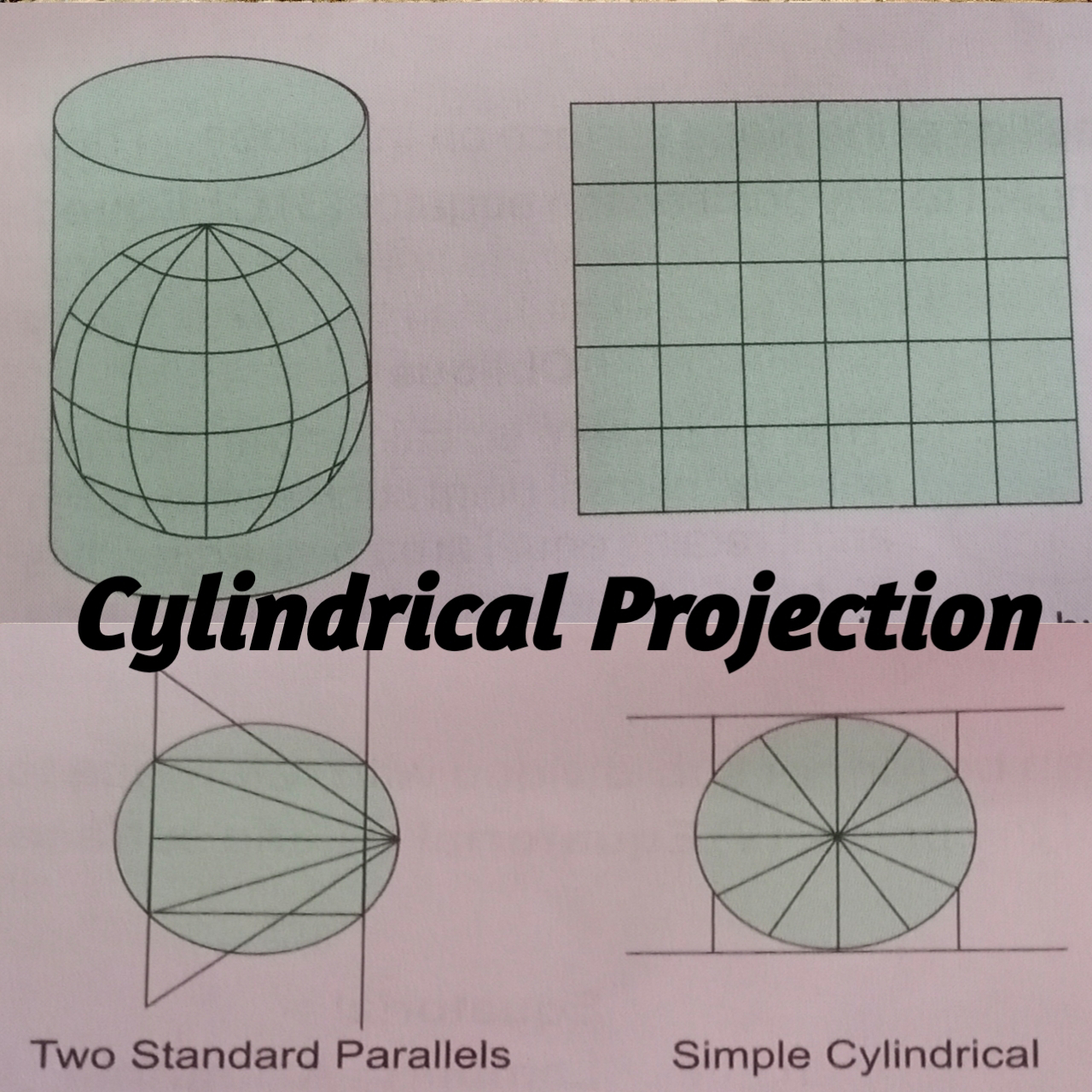
📝... [ B ] Cylindrical Projection:- Cylindrical projections are constructed by projecting the surface of the globe on to a cylinder just touching the globe in which the light is supposed to be a placed at the center of the globe. The scale is correct only along the equator.
📝.. Types of Cylindrical Projection :-
👉 ( 1.) Cylindrical Equal Area Projection :- In this projection the world can be shown on a map with the correct relative size and area.
👉 (2.) Mercator projection :- In this projection the latitudes are drawn parallel to the equator. The areas away from the equator are very much exaggerated. The pole (Which is actually a point) is represented by a line equal to the equator. The meridians are perpendicular to the equator and parallel to each other. This projection is not useful for representing areas in higher latitudes. But it is very important in navigational purposes since it shwos correct direction.
📝... [ c ] Zenithal Projections :- these projections are constructed by placing a plane tangent to the globe and light is focused on it from various positions to produce an image of the parallel and meridians on the plane. The plane can be tangent to a globe and can occupy several positions either at one of the poles , or at any point on the equator or at any other point.
In these projections the directions of all points from the center of the map remain correct , and therefore it is also called Azimuthal Projections.
✍️✍️✍️ The position of light is very important because the distances between various lines of latitude and longitude will be determined by the relative positions of the point to be projected and the source of light.
✍️✍️✍️ Accordingly the Zenithal projections can be divided in to three types.
1. Gnomonic zenithal Projection :- In this projection the light is placed at the center of the globe.
2. Stereographic zenithal Projection :- In this projection the light is placed at a point diametrically opposite to the point where the plane touches the globe.
3. Orthographic Zenithal Projection :- In this projection the light is at infinity so that the rays of light are parallel.
✍️✍️✍️ Each of these three types of zenithal projections can be further sub-divided with reference to the position of the plane surface on the globe. They are :-
1. Polar Zenithal Projections :- it's simple to construct. The five different methods comparing area, distortion etc.
( a.) Equal area
( b.) Equi Distance
( c.) Orthographic
( d.) Gnomonic
( e.) Stereographic
2. Equatorial Zenithal Projection :- In this projections both equal area and bearings is true from the center. for example Lambert Azimuthal equal area projection.
3. Oblique Zenithal Projection :- The projection is calculated from a selected central point such as the poles. It retains equal area properties. It is a good projection to show large continental masses.
📝... Conventional Projections :- some projection can be constructed purely by mathematical computation. These projections complete our special needs are called conventional projection.
Example -
1. Mollweides projection.
2. Interrupted sinusoidal projection.
3. Globular projection.
4.Hammers projection.
5. Sinusoidal projection.
6. nterrupted Mollweides projection.
(1.) Mollweides Projection :- it is an equal area projection. This shape is well maintained in the equatorial, tropical and mid latitude areas.
(2.) Interrupted sinusoidal Projection :- it is also known as Sanson Flamsteeds Projection. To improve the shape of the continents. The projection can be interrupted , through at the expense of continuous sea areas.
Thanks for Reading...... Like comment and share subscribe my blog... 🙏🙏🙏



















0 टिप्पणियाँ
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.